Education
(31) Debriefing Quality, Debriefer and and Student Engagement in Nursing Education
Friday, June 20, 2025
3:15 PM - 4:15 PM MST
Location: Plaza Ballroom Foyer

Monina Franco-Tantuico, PhD, MSN, BSMT, RN, CNE (she/her/hers)
RBHS Lecturer and Simulation & Clinical Learning Faculty
Rutgers, The State University of New Jersey, School of Nursing
Cranford, NJ, United States
Lead Author(s)
Abstract :
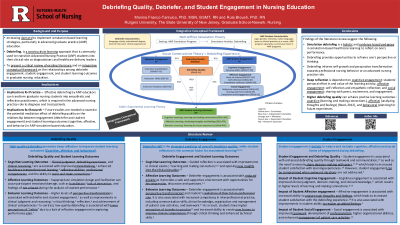
Introduction: Simulation debriefing is a critical component of reflective learning; however, little is known about high-quality debriefing and its relationship with debriefer engagement, student engagement, and student learning outcomes in graduate nursing education.
Methods: The databases: Cumulative Index to Nursing and Allied Health Literature (CINAHL), Medline, Academic Search Premier, ProQuest dissertation, PubMed, and Google Scholar were searched using key terms: active learning, debriefing, debriefer skills, student engagement, debriefing quality, and student learning outcomes. The search included primary and peer-reviewed studies published in English in 2018 – 2023, which led to 25 articles for the final review.
Results: Quality debriefing is associated with debriefer and student engagement, improving clinical judgment and reasoning, critical thinking, reflection, and competencies. Debriefer skill is considered the strongest predictor of overall simulation quality, while student reflection is the common factor for maximized learning. An expert debriefer guides reflection to improve performance in clinical exams and perspective transformation, directs control of the clinical situation, and reduces anxiety. Student engagement enhances the debriefing quality and student behavior through teamwork, communication and decision-making with peers, leading to satisfaction with learning. However, student engagement can be compromised when awkward situations are not addressed.
Conclusion: This paper describes how debriefing quality could depend on the student’s cognitive, affective, and social engagements and the debriefer’s skill to achieve cognitive, affective, and behavior learning. However, limited empirical studies examine these associations in graduate nursing education, including the mediation effect of debriefing quality between engagement and student learning outcomes.
Please include a short summary of your presentation that highlights why an attendee would want to participate in your session.: Simulation-based learning combined with debriefing has become a core component of nursing education to meet competency requirements and to promote the transfer of learning into clinical practice. However, the quality of debriefing methods remains varied across faculties and facilities. This literature review presents debriefing quality, engagement, and learning outcomes in simulation-based healthcare education, focusing on graduate nursing education.
Introduction: Simulation debriefing is a critical component of reflective learning; however, little is known about high-quality debriefing and its relationship with debriefer engagement, student engagement, and student learning outcomes in graduate nursing education.
Methods: The databases: Cumulative Index to Nursing and Allied Health Literature (CINAHL), Medline, Academic Search Premier, ProQuest dissertation, PubMed, and Google Scholar were searched using key terms: active learning, debriefing, debriefer skills, student engagement, debriefing quality, and student learning outcomes. The search included primary and peer-reviewed studies published in English in 2018 – 2023, which led to 25 articles for the final review.
Results: Quality debriefing is associated with debriefer and student engagement, improving clinical judgment and reasoning, critical thinking, reflection, and competencies. Debriefer skill is considered the strongest predictor of overall simulation quality, while student reflection is the common factor for maximized learning. An expert debriefer guides reflection to improve performance in clinical exams and perspective transformation, directs control of the clinical situation, and reduces anxiety. Student engagement enhances the debriefing quality and student behavior through teamwork, communication and decision-making with peers, leading to satisfaction with learning. However, student engagement can be compromised when awkward situations are not addressed.
Conclusion: This paper describes how debriefing quality could depend on the student’s cognitive, affective, and social engagements and the debriefer’s skill to achieve cognitive, affective, and behavior learning. However, limited empirical studies examine these associations in graduate nursing education, including the mediation effect of debriefing quality between engagement and student learning outcomes.
Please include a short summary of your presentation that highlights why an attendee would want to participate in your session.: Simulation-based learning combined with debriefing has become a core component of nursing education to meet competency requirements and to promote the transfer of learning into clinical practice. However, the quality of debriefing methods remains varied across faculties and facilities. This literature review presents debriefing quality, engagement, and learning outcomes in simulation-based healthcare education, focusing on graduate nursing education.
Learning Objectives:
- Discuss the theoretical frameworks relevant to simulation-based education and active learning in nursing education.
- Explain the relevance of the nurse educator’s active learning expertise and student engagement during simulation debriefing in maximizing cognitive, affective and behavior student learning outcomes.
- Discuss high-quality debriefing, an evidence-based pedagogy in healthcare simulation-based education, as most beneficial to achieving expected student learning outcomes.